The Shale Boom and U.S. LPG Dominance: How America is Reshaping Global Energy Markets

The United States has transformed itself into a global energy powerhouse, largely thanks to the shale revolution. Once a net importer, the U.S. now plays a pivotal role in supplying LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) to the world, reshaping global energy markets and positioning itself as a reliable energy partner for key regions like Europe and Asia. But while the industry has achieved impressive growth, challenges remain that could affect its trajectory.
The Rise of U.S. LPG: A Shale-Driven Success Story
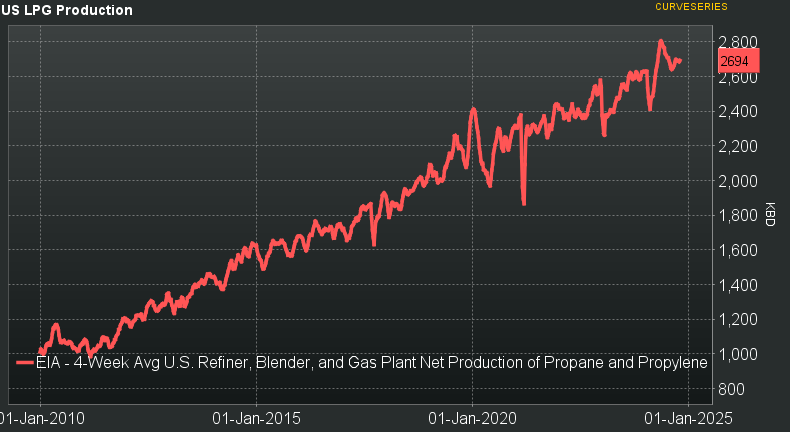
Source: EIA
The shale revolution has transformed the U.S. into a global leader in LPG production. Starting around 1 million barrels per day in 2010, production surged to over 2.6 million barrels per day by 2023. This growth is a direct result of technological advancements in hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling, which unlocked vast shale gas reserves.
The shale boom of 2014-2015 saw significant increases in natural gas liquids (NGLs) production, including LPG, particularly from the Marcellus and Utica formations. By 2018, another major boost came from the Permian Basin, where crude oil and associated gas production drove LPG output above 2,000 thousand barrels per day. The U.S. LPG market has since expanded rapidly, allowing the country to become one of the world’s largest exporters.
Key importers, such as China, Japan, and Europe, have increasingly turned to U.S. LPG as they diversify energy sources, particularly in the wake of the Russia-Ukraine conflict. The geopolitical impact is substantial, as the U.S. now plays a crucial role in stabilizing global LPG markets. This shift underscores the strategic importance of the U.S. in global energy security and supply chains, solidifying its position as a vital player in both the economic and geopolitical spheres of energy.
U.S. as a Global LPG Export Powerhouse
Today, the U.S. exports significant volumes of LPG to key markets in Asia and Europe, competing with established players like Qatar and Saudi Arabia.
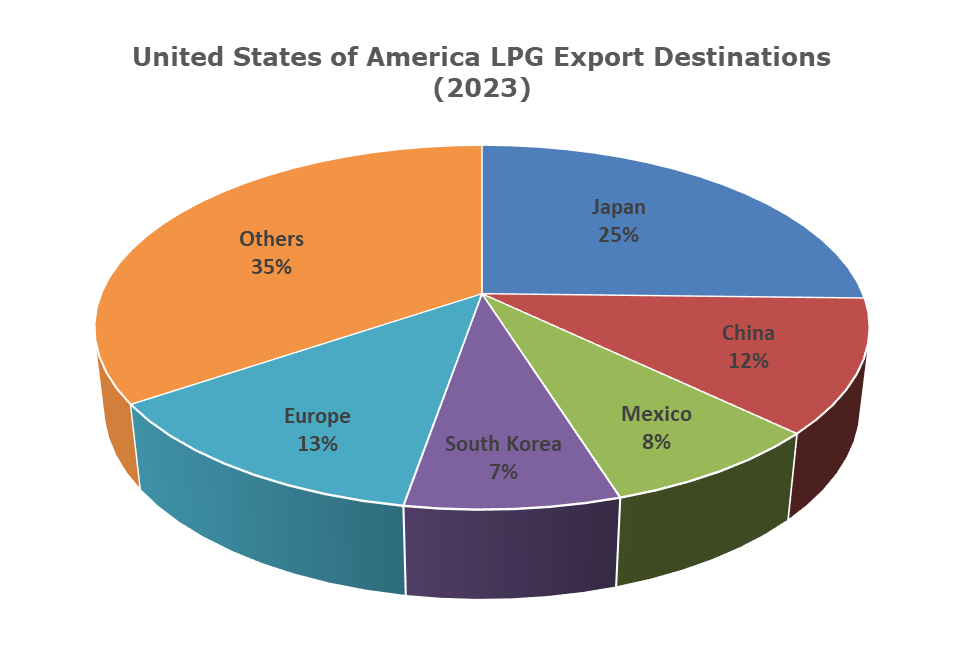
Source: Trademap
Japan is the largest importer, receiving 25% of U.S. LPG exports, reflecting its heavy reliance on U.S. energy to meet domestic demand. China follows with 12%, driven by its expanding industrial needs and efforts to reduce coal dependence. South Korea accounts for 7%, using U.S. LPG in its petrochemical and industrial sectors.
Europe receives 13%, increasingly relying on U.S. LPG following the Russian energy crisis, which has forced the continent to diversify its energy imports. Mexico also takes 8%, using LPG for residential and industrial purposes.
The remaining 35% is distributed among other countries, illustrating the U.S.’s broad reach in global energy markets. The U.S.’s vast shale gas reserves have enabled it to become a major player in the LPG market, strengthening its influence on the global energy transition.
Challenges Facing the U.S. LPG Industry

Despite its global dominance, the U.S. LPG industry faces significant challenges that could impact its future growth. LPG prices are closely tied to global oil and gas markets, which are highly sensitive to geopolitical events and economic shocks. For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic caused a sharp drop in demand, leading to lower prices, while the Russia-Ukraine conflict created sudden spikes. Such fluctuations make it difficult for producers to plan and maintain profitability.
Environmental concerns also pose a growing challenge. Although LPG is often promoted as a cleaner alternative to coal and oil, it is still a fossil fuel and thus subject to increasing regulatory pressures aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the industry’s reliance on fracking for LPG production raises concerns about water contamination, land use, and methane emissions, which contribute to climate change.
Lastly, competition from alternative energy sources such as LNG (liquefied natural gas) and renewables is intensifying. As countries around the world work toward decarbonization, demand for renewable energy and lower-emission fuels is rising. This shift could eventually reduce the demand for LPG, especially if cleaner technologies continue to become more cost-effective and accessible. To stay competitive, the U.S. LPG industry must adapt by addressing environmental concerns and preparing for a more sustainable energy landscape.
Looking Ahead: Can U.S. LPG Maintain Its Dominance?

The U.S. LPG industry has proven itself resilient, adapting to global disruptions and emerging as a critical player in the energy sector. However, sustaining this dominance will require navigating a landscape that’s increasingly focused on environmental accountability and energy diversification. To remain competitive, the industry must address environmental concerns, invest in sustainable practices, and find ways to coexist with renewable energy sources.
In an evolving global energy market, the U.S. LPG sector stands at a crossroads. Its ability to balance economic goals with environmental responsibilities will determine its relevance in a world that’s moving toward a greener future. For now, the U.S. remains a dominant force, but the journey ahead will require innovation, adaptability, and a commitment to meeting the world’s changing energy needs.




